sackur tetrode equation
Associative of partition function
Z=α∑e−βEα=i∑j∑e−β(Ei(a)+Ej(b))
=(e−βE1(a)+e−βE2(a)+⋯)(e−βE1(b)+e−βE2(b)+⋯)=Za⋅Zb
Partion function of ideal gas
E=21mv2
Z=α∑e−β21mvα2→∫0∞e−βfrac12mv2g(v)dv
g(v) is density of states
Quantumn magic
Infinte square wall
ψn=√L2sin(kx),(k=Lnπ)
ψ(x,y,z)=ψn(x)ψn(y)ψn(z)=√L2sin(kxx)√L2sin(kyy)√L2sin(kzz)
=L23/2sin(kxx)sin(kyy)sin(kzz)
because expectation energy is
⟨E⟩=2mℏ2L2n2π2
in case of 3-D space,
⟨E⟩=2mℏ2(Lx2nx2π2+Ly2ny2π2+Lz2nz2π2)
=2mℏ2(kx2+ky2+kz2)=2mℏ2k⃗2
ki=Liniπ,i=x,y,z
k⃗2=2mℏ2⟨E⟩
Z=α∑e−βE=∑e−β2mℏ2k⃗2
Density of state
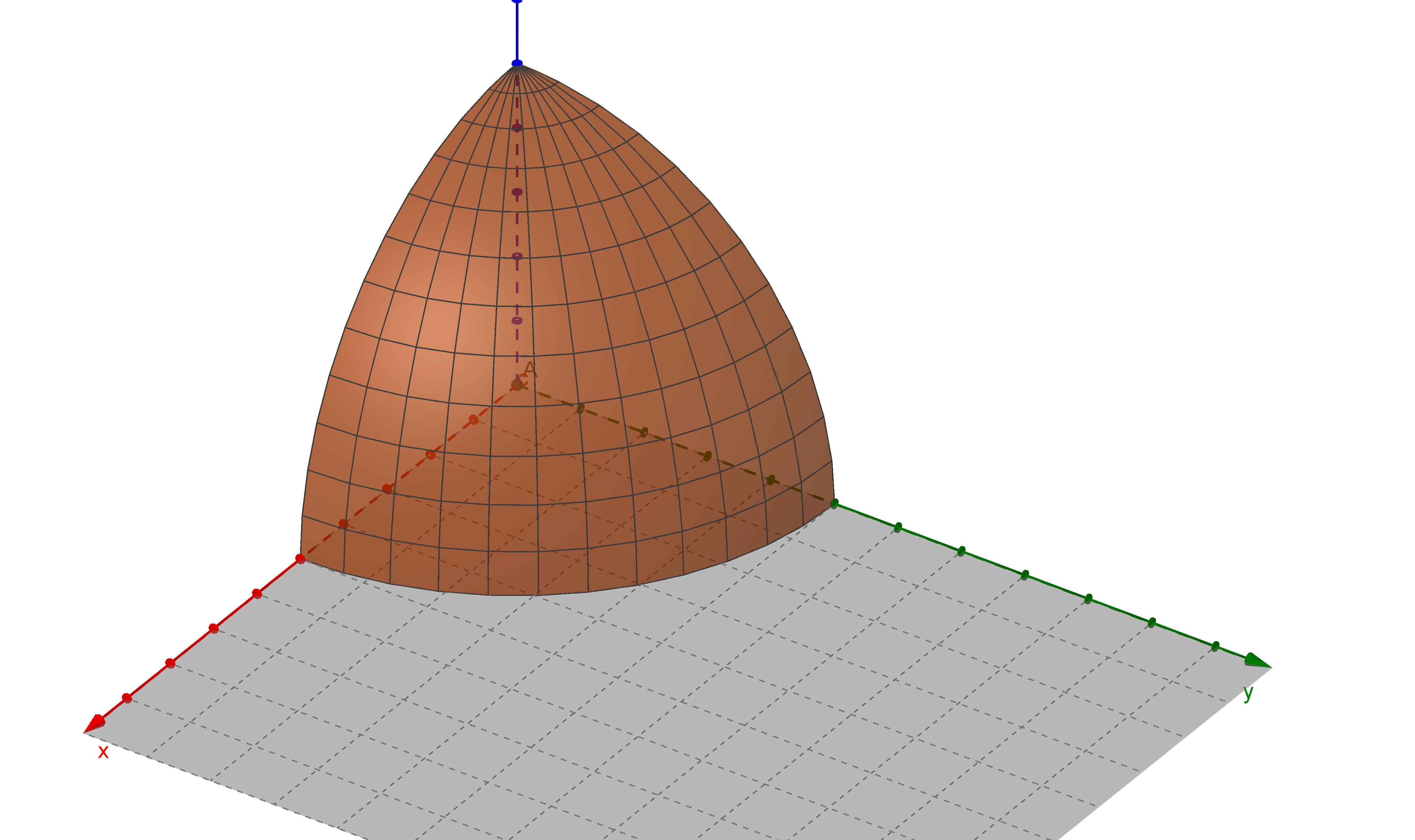
surface: 81(4πk2)
volume: surface ×dk
density of state:volume k-space occupied per allowed statevolume in k-space of one of a shell
=(Lπ)3volume=2π2k2L3dk=2π2k2Vdk=g(k),number of state in (k,k+dk)
Thermal wavelength
Z=∫0∞e−β2mℏ2k⃗22π2k2Vdk=8π2V(β3ℏ68m3π)21
=ℏ3V(2πmkT)23,β=kT1
=V⋅nQ,(nQ−1/3=√2πmkTℏ,[m])
nQ is quantum concentration.
the de-brogil wavelenth is λ=pℏ, we set √2πmkT be average thermal momentum.
λth=√2πmkTℏ,thermal wave length
Indistinguishable
U(internal energy), F(helmholzt), S(entropy) Partition function
U=−dβdln(Zn), F=−kbTln(Z), S=TU−F
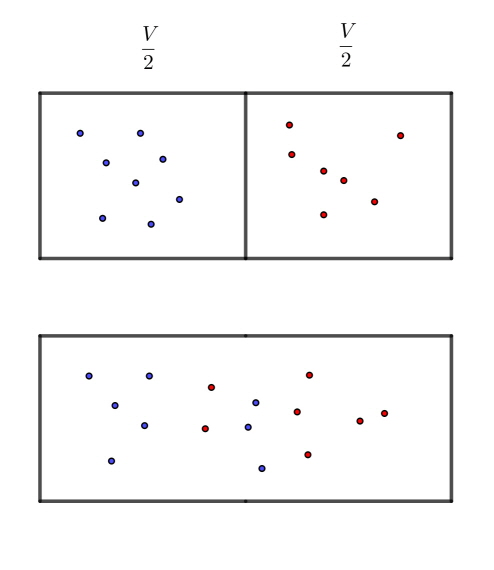
Gibb's paradox
The partition function of N free particles is
Zn=Zn=(ℏ3V(2πβm)23)N==(V⋅nQ)N
U=−Ndβdln(ℏ3V(2πβm)23)=N23dβdln(2πβ)=N23kT
F=−kTNln(V⋅nQ)
S=N23k+kNln(V)
Sbefore=2(2N23k+k2Nln(2V))
Safter=N23k+kNln(V))
Safter−Sbefore=kNln(V)−kNln(2V)≠0
Indistinguishability of the particles
Zn=N!Z1n
Zn=N!Zn=N!1(ℏ3V(2πβm)23)N=N!(V⋅nQ)N
U=−Ndβdln(N!1ℏ3V(2πβm)23)=N23dβdln(2πβ)=N23kT
F=−kT(Nln(V⋅nQ)−ln(N!))=−kT(Nln(V⋅nQ)−Nln(N)+N)=−kTNln(NV⋅nQ⋅e)
S=kN(23+ln(NV⋅nQ⋅e))=kNln(NV⋅nQ⋅e5/2),Sackur-tetrode equation
Sbefore=2(k2Nln(NV⋅nQ⋅e5/2))
Safter=kNln(NV⋅nQ⋅e5/2))
Safter−Sbefore=0


